Introduction
Using swift in xcode, the object of this project was to create a fully functioning
Game Rules
The objective of the game is to select the color cell with the different color, which becomes slighter as the game processes. Also, as the palyer goes through the rounds, the total number of cells also increase, making it harder for the player to choose the correct cell.
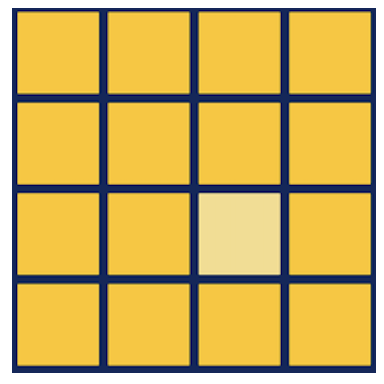
UI Model
The stages (phases) of the game is the following:
- Introduction - Provides general information about the game and sets a start button at the bottom.
- Rounds - Player simply goes through the rounds, with an option to restart.
- Termination of the game a: Cleared - Player completes the game up to the last round, where the game restarts. b: Busted - Player selects a wrong cell in the process of the game, where the game restarts.
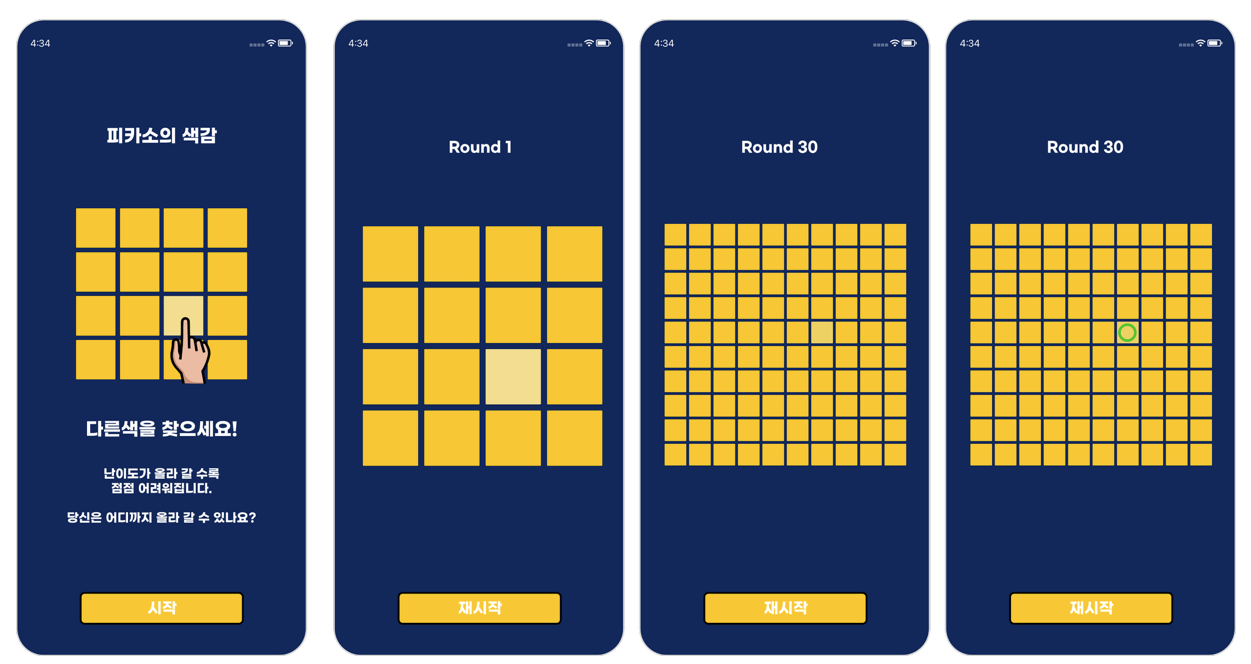
As shown above, the ui model shown follows the listed logic which will be further explained through the swift language below.
Variables
@Published var gameState: GameState = .notStarted // 1. Initial condition of the game --> notstarted
@Published var round: Int = 0
@Published var numberOfRows = 10 // 2. Size of the cells.
@Published var mainCellColor: Color = .blue // 3. Color of the cell
@Published var differentColor: Color = .blue
@Published var differentColorIndex: Int = 0
let maxRound = 5 // 4. Maximum Number of rounds
Game Phases
func startGame() { // 1. Game started, prepares next round
gameState = .playing
prepareNextRound()
}
func finishGame() { // 2. Game finished, proceeds to clear message
gameState = .cleared
}
func resetGame() { // 3. Game restarted
round = 0
startGame()
}
func bustGame() { // 4. Busted
gameState = .busted
}
The phases of the games are shown above, where depending on the player’s actions, the next step of the game is chosen.
Next Round
func prepareNextRound() {
round += 1
setMainCellColor()
selectDifferentColorCellIndex()
setDifferentColor()
}
Between each round, the cell colors, the number of cels, and the different-color cell is chosen.
Cell Setup
private func setMainCellColor() {
// 1. Selects RGB Value between 50~200.
let randomRed = Double(Int.random(in: 50...200))
let randomGreen = Double(Int.random(in: 50...200))
let randomBlue = Double(Int.random(in: 50...200))
mainCellColor = Color(.sRGB, red: randomRed / 255, green: randomGreen / 255, blue: randomBlue / 255, opacity: 1.0)
}
// 2. Selects the number of cells
private func selectDifferentColorCellIndex() {
differentColorIndex = Int.random(in: 0..<numberOfRows * numberOfRows)
}
// 3. Creates the different colored cell
private func setDifferentColor() {
// 4. Recreates the main cell color in terms of RGB
let red = mainCellColor.cgColor!.components![0] * 255
let green = mainCellColor.cgColor!.components![1] * 255
let blue = mainCellColor.cgColor!.components![2] * 255
// 5. The changed color component between Red, Green and Blue is chosen.
let index = Int.random(in: 0...2) // 6. Chooses a random number for the RGB change
let plusOrMinus = Bool.random() // 7. Either adds or subtracts 50 from the RGB value
let offset = CGFloat(50) // 8. Difference in RGB (Offset value initially set to 50)
if index == 0 { // 9. Either adds or subtracts the offset value for the changed color value
let newRed = plusOrMinus ? red + offset : red - offset
differentColor = Color(.sRGB, red: newRed / 255, green: green / 255, blue: blue / 255, opacity: 1.0)
} else if index == 1 {
let newGreen = plusOrMinus ? green + offset : green - offset
differentColor = Color(.sRGB, red: red / 255, green: newGreen / 255, blue: blue / 255, opacity: 1.0)
} else if index == 2 {
let newBlue = plusOrMinus ? blue + offset : blue - offset
differentColor = Color(.sRGB, red: red / 255, green: green / 255, blue: newBlue / 255, opacity: 1.0)
}
Through this process, the colors and the orientation of the cell are prepared between each round.
Game States
@ViewBuilder private func cell(index: Int) -> some View {
if index == viewModel.differentColorIndex {
viewModel.differentColor
.onTapGesture {
// 1. When tapped correctly, proceeds to next round
if viewModel.round == viewModel.maxRound {
// 2. If last round, terminates the game
viewModel.finishGame()
} else {
viewModel.prepareNextRound()
}
}
} else {
viewModel.mainCellColor
.onTapGesture {
// 3. Busts game if the color selected is the main color (but not the altered color)
print("Wrong cell! Game Busted!")
viewModel.bustGame()
}
}
}
Through this process, the next game state is chosen, where then the functions inside the game phases are operated accordingly.
Conclusion
This study focuses on the view model of the game simulation, rather than the visual elements itself. The user interaction is explained through the various functions used in the study, where the functions are organized in a visually appealing orientation.